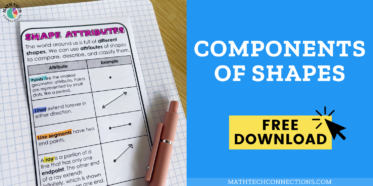
In 3rd grade, students begin to develop a more formal understanding of geometric shapes based on their defining attributes. Attributes of shapes in 3rd grade are based on geometric components like right angles and intersecting, perpendicular, and parallel lines.
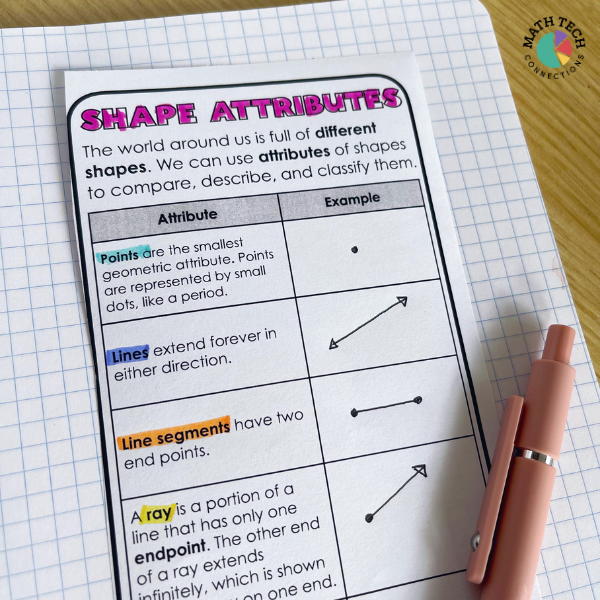
MA.3.GR.1.1 – Describe and draw points, lines, line segments, rays, intersecting lines, perpendicular lines, and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures.

Open vs. Closed Shapes
Formal geometric shapes are closed. They start and end at the same point. Open shapes have different starting and ending points and can be described as unfinished. Closed shapes can be further categorized based on their combination of geometric components. For example, circles and ovals have no straight sides or angles because they are composed of a single curved line.

Polygons
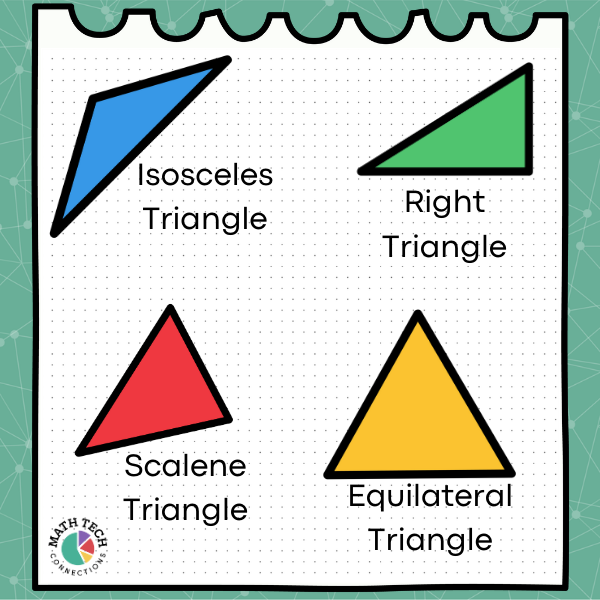
Understanding polygons is where geometry really starts to become fun! Simply defined, polygons are closed shapes with straight sides that intersect to form corners or angles.
Triangles are polygons with the least number of possible straight sides. Three sides are needed to form a closed shape with straight sides and have a defined interior area.
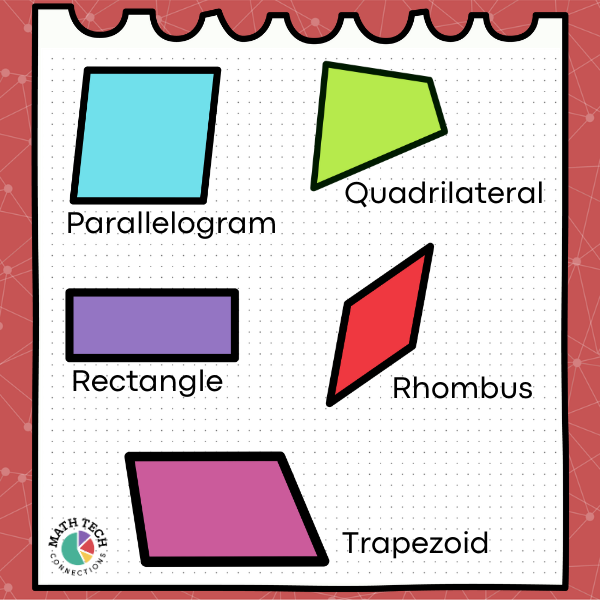
Quadrilaterals
Polygons with four sides are called quadrilaterals. The main categories of quadrilaterals are parallelograms, rhombuses, rectangles, squares, and trapezoids. There are also quadrilaterals that don’t belong in any of these categories. The defining attributes of quadrilaterals are 4 straight sides and 4 angles. Sub-categories within quadrilaterals have additional defining attributes that involve parallel and perpendicular line segments (sides).
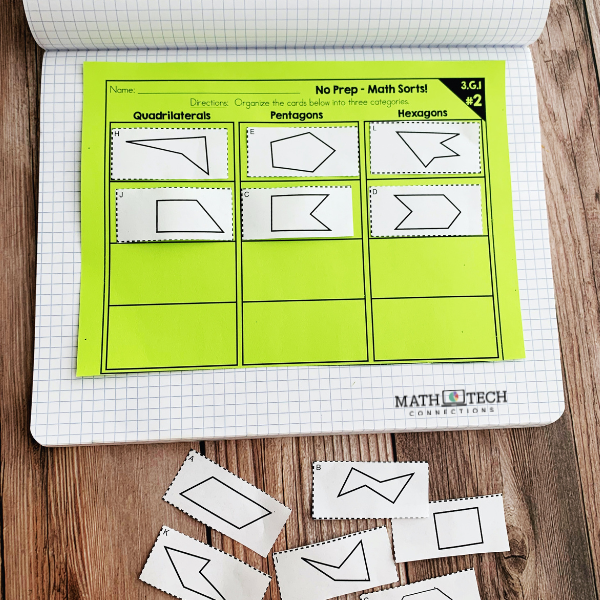
Pentagons & Hexagons
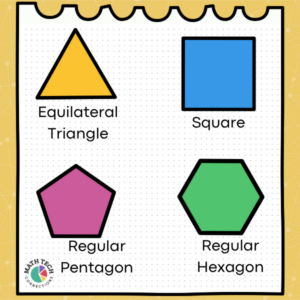
Pentagons are polygons with 5 sides and angles, and hexagons have 6 sides and angles. Triangles, pentagons, and hexagons are a great way to get students started classifying quadrilaterals. Hands-on sorting and drawing activities help students describe defining attributes.
Regular Shapes
Within each larger polygon category are shapes that always look the same and shapes that can look very different. Shapes that always look the same are regular, which means they have equal sides. For example, triangles can have a right angle, 3 acute angles, or have an obtuse angle. Equilateral triangles always look the same because they can only change in size without altering their defining attributes: 3 equal sides and 3 equal angles. Squares always look the same because they can only change in size.
Other quadrilaterals like rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids on the other hand can look quite different while retaining their defining attributes. Regular pentagons and hexagons also have a distinct look, while other pentagons and hexagons can present a variety of ways.
Standards
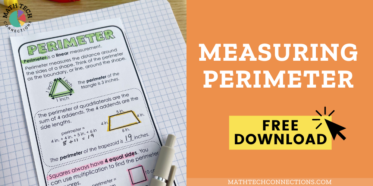
Geometry standards for understanding and classifying polygons are fairly consistent across the country. Students will progress in following years to an even more sophisticated understanding of shapes and measuring the perimeter and area of 2-dimensional shapes, first with whole numbers, then with fraction and decimal side lengths.
A solid understanding of the defining attributes of shapes provides a strong foundation for meeting grade level expectations in geometry for years to come.
















Leave a Comment